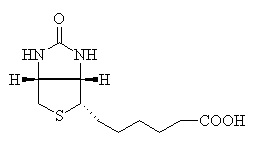
Biotin Vitamin B7 Molecule

Biotin, also known as vitamin H or B7 and C10H16N2O3S (Biotin; Coenzyme R, Biopeiderm), is a B-complex vitamin which is important in the catalysis of essential metabolic reactions to synthesize fatty acids, in gluconeogenesis, and to metabolize leucine.
The molecular weight of biotin is 244.31.
Biotin deficiency is rare. The amounts needed are small, a wide range of foods contain biotin, and intestinal bacteria synthesize biotin, which is then absorbed by the host animal. For that reason, statutory agencies in many countries, for example the USA and Australia, have not formally established a recommended daily intake of biotin.
Food Sources of Biotin
In order to include a fair amount of biotin in the diet, you should consume foods like egg yolks, fish, milk, meat liver, and kidney. Also important is that egg whites restrict the absorption of this vitamin and should, therefore, be avoided in large quantities.
Likely effectiveness for Biotin B7 -- for Biotin Defiency --
- Biotin deficiency. Taking biotin can help treat low blood levels of biotin. It can also prevent blood levels of biotin from becoming too low. Low blood levels of biotin can cause thinning of the hair and rash around the eyes, nose, and mouth. Other symptoms include depression, lack of interest, hallucinations, and tingling in the arms and legs. Low biotin levels can occur in people who are pregnant, who have had long-term tube feeding, who are malnourished, who have undergone rapid weight loss, or who have a specific inherited condition. Cigarette smoking might also cause low blood levels of biotin.
Source--Medline Plus
Vitamins
| Biotin(B7) |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
| Vitamin D |
| Vitamin K |
| Vitamin E |
| Vitamin A |
| Folic Acid (B9) |
| Thiamine (B1) |
| Vitamin C |
| Niacin (B3) |
| Pyridoxine (B6) |
| R-panthothenate |